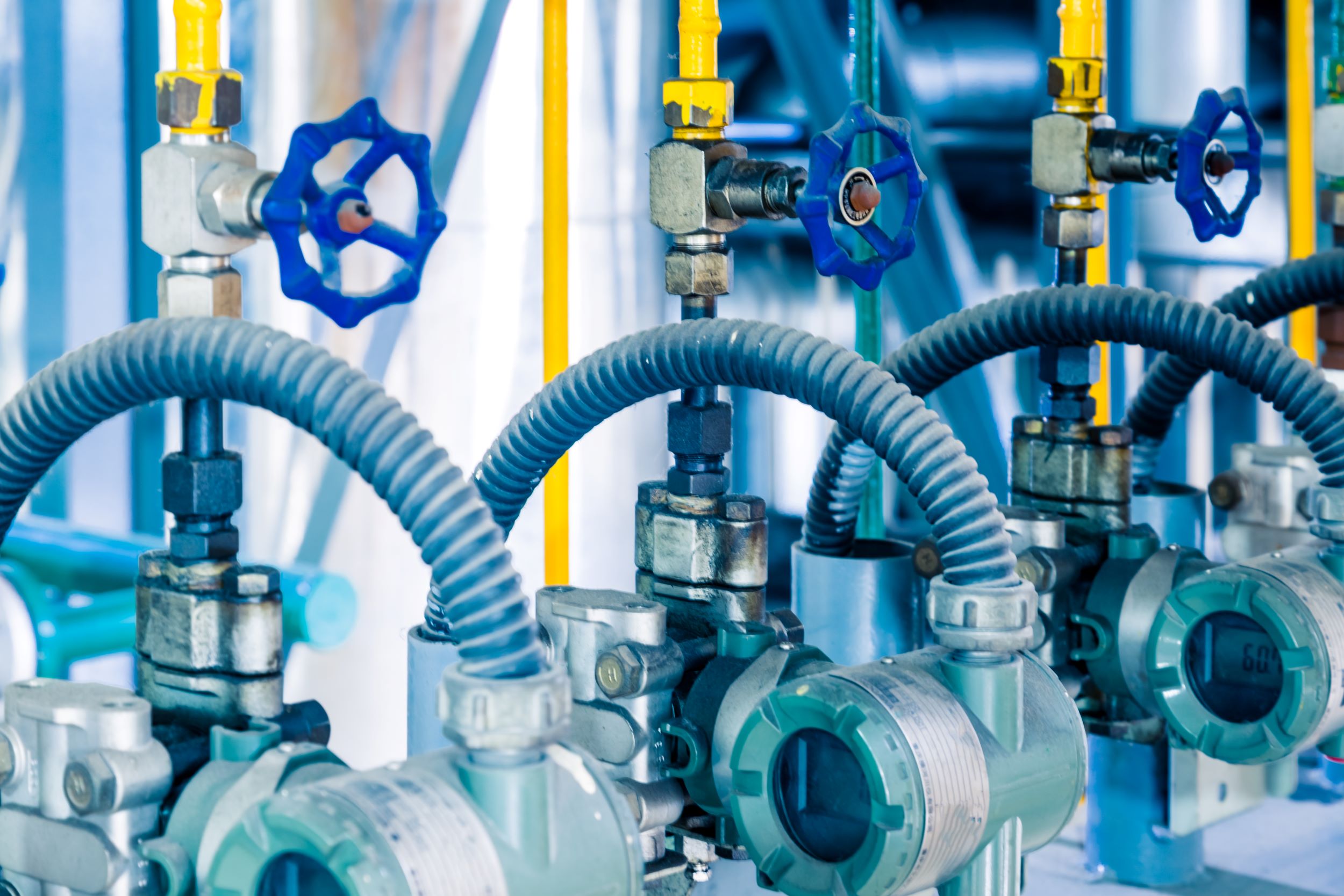
Pneumatic cylinders might sound like something straight out of an engineer’s toolkit, but these are tools as part of pneumatic equipment that play a significant role in industries ranging from manufacturing to packaging and even robotics. But how exactly is a pneumatic cylinder used? Let’s talk about it.
What Is a Pneumatic Cylinder?
Air or pneumatic cylinders turn compressed air energy into linear motion. Imagine a tube with a piston inside, driven by air pressure to create movement. This motion can push, pull, lift, or position objects in a wide variety of applications.
There are two main types of pneumatic cylinders:
- Single-acting cylinders: These use air pressure to move the piston in one direction, with a spring returning it to its original position.
- Double-acting cylinders: These use air pressure for motion in both directions, offering more control and flexibility.
Getting Started with a Pneumatic Cylinder
A pneumatic cylinder operates as part of a larger pneumatic system, which typically includes an air compressor, valves, hoses, and a control mechanism. Here’s a quick overview of what you need:
1. Air Compressor: Supplies the compressed air needed to power the cylinder.
2 . Air Lines and Fittings: Connect the cylinder to the compressor and other components.
3 . Valves: Regulate the airflow, allowing you to control the cylinder’s motion.
4 . Lubrication System: Ensures smooth operation and reduces wear and tear.
How to Use a Pneumatic Cylinder
1. Understand the Application
Before you start, be clear about the task your pneumatic cylinder will perform. Are you lifting objects, moving components, or holding items in place? The type of cylinder you use and how you control it depends heavily on the application.
2. Install the Cylinder Correctly
Start by securely mounting the pneumatic cylinder in place. Most cylinders come with mounting options like flanges, clevises, or trunnions. Make sure the cylinder is aligned with the motion it’s supposed to generate. Misalignment can lead to uneven wear, reduced efficiency, or even damage.
3. Connect to the Air Supply
Attach the airlines to the cylinder’s ports using the appropriate fittings. For a single-acting cylinder, you’ll only need one air line connected to the pressure port. For double-acting cylinders, you’ll connect two airlines—one for extending the piston and another for retracting it.
4. Set Up the Control Valves
Control valves are the brains of your pneumatic system. They determine when and how air flows into the cylinder. Use a two-way valve for single-acting cylinders or a four-way valve for double-acting ones. Adjust the valves to regulate speed and force, ensuring smooth operation.
5. Test the System
Once everything is connected, it’s time for a test run. Slowly introduce air into the system and observe the cylinder’s movement. Look for smooth, consistent motion. If the cylinder jerks or hesitates, check for air leaks, blockages, or misaligned components.
Tips for Efficient Operation
Getting the best performance out of a pneumatic cylinder starts with controlling its speed. Flow control valves are key here, allowing you to fine-tune the movement for smooth, precise operation. Without proper speed control, the cylinder may jerk or operate inefficiently, potentially affecting the overall system.
Monitoring air pressure is equally important. Excess pressure can strain the cylinder or connected components, leading to unnecessary wear or damage. Keeping the pressure within the recommended range not only extends the life of the system but also ensures consistent performance.
Lubrication plays a critical role in maintaining efficiency. Some cylinders require regular lubrication to minimize friction and keep operations smooth. Installing a lubricator in the air supply line can simplify this process by automatically providing the necessary lubrication, saving you time and effort.
Finally, regular inspections are non-negotiable. Checking hoses, fittings, and seals for wear or damage can prevent minor issues from turning into costly problems. Preventative maintenance might not feel urgent, but it’s the best way to avoid unexpected downtime and keep everything running like clockwork.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Misalignment can place unnecessary stress on your cylinder, reducing its efficiency and potentially causing long-term damage. Taking a moment to ensure everything is properly aligned can save you time and effort in the long run.
Air quality is another critical factor. Moisture or debris in the system can lead to corrosion or clogs, which are avoidable with a simple air filter. It’s a small addition that goes a long way in keeping your cylinder running smoothly.
Routine maintenance might not seem urgent, but skipping it can lead to big problems. A quick check of seals, hoses, and fittings can prevent costly breakdowns and keep your system operating at its best.
CONCLUSION
Using premium SS Hussain pneumatic cylinders and professional advice, set up your pneumatic system to guarantee flawless operation of your gear.