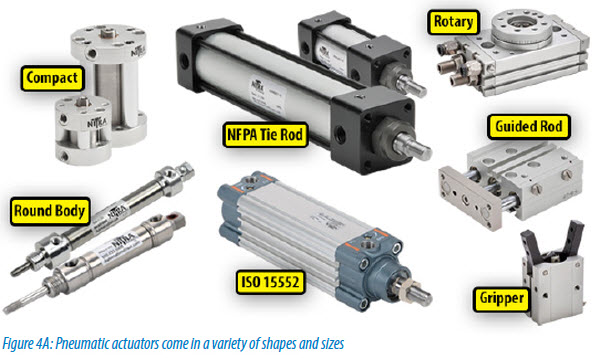
An air cylinder or a pneumatic actuator are other names for a pneumatic cylinder. Mechanical elements utilize air or compressed gas to generate power or movement. They are an affordable, efficient technique to generate linear or rotary motion. Pneumatic drives and actuators are other names for pneumatic cylinders.
Applications: The functions of a pneumatic cylinder vary depending on the application. A pneumatic cylinder’s main purpose is to generate motion and force from air pressure through the inflow of pressurized gas; its precise function will depend on the application of the product. Pneumatic cylinders are frequently employed in the manufacturing sector to open valves, and doors, transfer items onto and off conveyor belts and lift heavy objects. Pneumatic cylinders serve varied purposes in the automotive sector. They are utilized for suspension and braking in cars and trucks.
How to choose the right cylinder for you: If you are unsure about what size cylinder you need for a particular application, you should always consult a specialist like the ones at SSHussain.
The websites of the manufacturers often include a wealth of information, and you may ask your regional representative. For your cylinder to last a long time, selecting the right one is crucial. A cylinder may bend and wear out very quickly if you utilized it for a task that was above its mechanical capacity. However, if you utilized a cylinder that was far bigger than it needed to be, you might be wasting air, which would not be productive. When selecting a cylinder, important factors to consider are the motion type (rotary or linear), pressure/load requirements, the environment the cylinder will be in, whether a single-acting or double-acting cylinder is required, and the required stroke length.
Types: In engineering and industrial areas, pneumatic cylinders are frequently chosen to generate motion from the buildup of compressed gas. The type of pneumatic cylinder you require will vary depending on the application and sector. Pneumatic cylinders are also referred to as air cylinders due to the manner the gadget operates.
- Guided cylinder: The piston of a magnetic cylinder, also known as a guided cylinder, has a magnet attached to it. This implies that by employing a reed switch or GMR switch, the precise location of the cylinder may be tracked and known at any time. This is especially helpful when utilizing a PLC or control system since it may provide feedback when the cylinder has finished a movement. When the valve has reached a given position, you can also swap to another valve in the control circuit to alter the speed. Some of the models used in the industry as standard are TN, MGPM, and
- Round cylinder: They are a type of single-acting cylinder. The piston in a single-acting air cylinder uses a single supply of air. This indicates that the piston can only be moved in one direction by air. An internal mechanical spring is used to move the cylinder in the opposing direction. In the event of a power outage, single-acting air cylinders (SAC) are the best option since they will reset to their initial state. The uneven output stroke of single-acting pneumatic cylinders is one of their drawbacks. The opposing force is a mechanical spring, which may ultimately wear out. As a result, the cylinder’s output stroke length fluctuates. Because of this, single-acting air cylinders would not be utilized in situations where precision is necessary. Some of the most commonly used Round cylinders are DSNU, MA, and MAL.
- Square cylinder: Another type of single-acting cylinder is the square cylinder. In contrast to double-acting pneumatic cylinders, which work on both ends of the piston, single-acting pneumatic cylinders only operate on one end of the piston. The single-acting cylinder is most frequently employed in internal engines, such as those seen in automobiles, where it depends on a force, such as springs or an external load, to move the piston in the opposite direction. Additionally, single-acting pneumatic cylinders can occasionally be seen in hydraulic rams and pumps. Some of the commonly used square cylinders are SC, DCN, and DSBC. These are available in Pakistan at sshussain .
- SDA cylinders: They are a type of telescopic cylinder. These pneumatic telescopic cylinders, also known as telescopic cylinders, come in double-acting and single-acting varieties. They have a piston rod that, when used, transforms into a segmented piston and extends the reach. In situations where little pressure is exerted, telescoping cylinders are frequently employed. The industry standard for these is SDA, ACQ, CQ2B, and CDU.
- Double-acting cylinders: In double-acting pneumatic cylinders, one element is employed for the outstroke and the other for the instroke of the piston. Double-acting pistons can be found in machinery like steam engines, which are regarded as external engines, even though single-acting pistons are more frequently utilized in internal engines. This is so that double-acting pneumatic cylinders produce both ends of the piston.
How to choose: If you are unsure about what size cylinder you need for a particular application, you should always consult a specialist. The websites of the manufacturers often include a wealth of information, and you may also ask your regional representative. For your cylinder to last a long time, selecting the right one is crucial. A cylinder may bend and wear out very quickly if you utilized it for a task that was above its mechanical capacity. However, if you utilized a cylinder that was far bigger than it needed to be, you might be wasting air, which would not be productive. When selecting a cylinder, important factors to consider are the motion type (rotary or linear), pressure/load requirements, the environment the cylinder will be in, whether a single-acting or double-acting cylinder is required, and the required stroke length.
Materials used: Pneumatic cylinders can be made from a variety of materials. What material is utilized depends on the operational conditions in which the cylinder will be used. The most typical materials are often steel, aluminum, stainless steel, brass, or some polymers.
Lubrication: Because of the enhanced seal material and design, cylinders do not need to be lubricated any longer. Today, manufacturers treat the inside components of the cylinder with greases during assembly to prevent drying out and degradation. Seals for pneumatic components are now typically made of nitrile and Teflon, which gives them more lubricity. In the past, lubricators were always included in air supply systems to allow for oil discharge into the compressed air system. During this time, pneumatic parts were not as well-sealed, which occasionally allowed water to enter and dry out.
Conclusion: For each specific operation, a distinct type of air cylinder—of which there are several in the industry—must be employed. The choice of each requires expert guidance. Since these are industry standards, we must utilize models that comply with them. Another important aspect of the procedure is costly. The potential trade-offs must be considered.