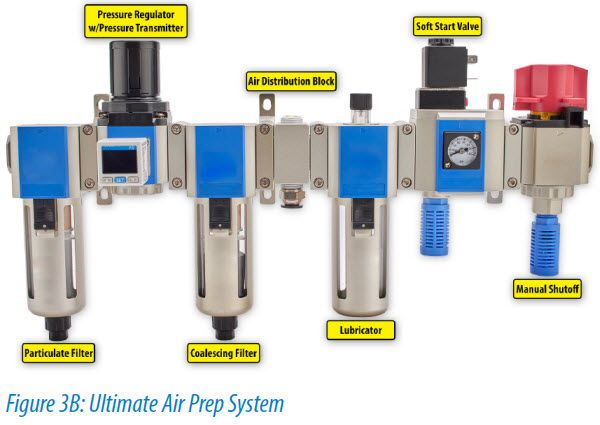
An essential but frequently ignored part of pneumatics is air preparation. It may appear insignificant or like unnecessary upstream complexity to perform “air prep,” as it is frequently referred to. In actuality, air preparation ensures that downstream equipment receives the proper air quality, pressure, and lubrication. The air that is released by the compressor in a pneumatic system is often unfit for any intended use. The compressed air is typically unclean, damp, and at improper pressure, which are qualities that could harm equipment further down the line. To condition compressed air to the proper purity, an FRL (Filter, Regulator, Lubricator) is utilized. An FRL unit is a system made up of three independent units that perform several conditioning steps, including filtration, control, and lubrication. It doesn’t necessarily arrive as a single unit, even though it is frequently utilized as a single system. It is instead common to utilize a single regulator unit or a filter-regulator unit. Modern pneumatic systems with self-lubricating machinery often do not utilize lubricators. For you to better grasp how air preparation units function in pneumatic systems, SS Hussain has put together this information. Our company is well-known for producing industrial measurement equipment in Pakistan.
Design Principles of Pneumatics:
Port sizes for all pneumatic components must match those of the inlet and outflow piping or tubing. Pneumatic devices may also be rated for a normal working pressure range, which may include a proof pressure, a burst pressure, or even all three. To function correctly, a gadget needs to be at its operating pressure. An operational pressure range for a solenoid valve, for instance, might be 20 to 100 psi. There is no assurance that the valve will function properly or at all if there is insufficient or excessive pressure. Ratings for proof and burst pressure are a little more challenging. The greatest air pressure that a device can withstand before failing and ceasing to function, even if normal pressure is restored, is known as the proof pressure. The greatest pressure a device can withstand before failing catastrophically, endangering users and maybe damaging other equipment, is known as burst pressure.
How Disconnects Work?
Always incorporate a way to disconnect air preparation machinery so that it can be disconnected as needed to remove harmful energy. Pressure is bled off or “relieved” using manual shut-off relief valves, which also isolate downstream equipment. Similar to an emergency stop mechanism, isolation/lockout valves function similarly to manual shut-off valves but are larger to swiftly place downstream equipment in a secure state. When turned on, soft-start valves gradually restore pressure even though they can immediately dump downstream pressure.
The Filter:
Eliminates any impurities like dust, water, vapor, or oil that may be in the air leaving the compressor. Maximizing the lifespan of downstream machinery requires effective filtration. Since filtering is the initial step in conditioning, the filter is typically put before other pieces of machinery. It functions by first forcing the entering air into a cyclonic action. The bottom of the bowl deposits heavy pollutants. After that, a filter mesh of the proper size is driven through the compressed air to remove impurities. Depending on the filter type, either manual or self-draining methods are used to gradually eliminate the collected pollutants and moisture. Self-draining filters have an automatic float-controlled valve that regularly drains the filter, whereas manual filters need the machine to be turned off to be emptied. The degree of filtration, there are three different types of filtration. they are:
- general-purpose filters that eliminate water and particulates
- filters for removing oil that also remove oil and vapor
- Removal devices that also remove vapor in addition to dust, oil, and water.
Function Of A Pressure Regulator:
In a pneumatic system, the regulator regulates compressed air pressure. It controls how much air pressure is delivered to equipment further down the line. For fluid power devices like blowguns, pneumatic cylinders, and air logic valves, in particular, this unit is essential. Also known as pressure reduction valves, regulators regulate pressure. An on-the-regulator control knob is used to establish the desired pressure for a particular application. For the proper output pressure, the internal diaphragm and needle valve assembly are adjusted using this knob. Relieving and non-relieving regulators are the two main categories. From high to low pressures, relieving regulators can be changed. These regulators will release too much downstream pressure when it’s essential. Conversely, downstream pressure cannot be reduced by non-relieving regulators. As a result, different techniques for releasing trapped air must be used. Regulators can be purchased separately or as a filter and regulator combined unit.
Process Of Lubrication:
A lubricator adds regulated amounts of oil to the compressed air flow. Oil-fog and micro-fog are two different categories of lubricators. In oil-fog lubricators, oil is directly injected into the airflow as rather big droplets. In contrast, micro-fog lubricators atom oil droplets down to around 2 m in size before dispersing them into the airflow. Lubrication is required to lessen the friction produced in moving parts. Lubrication is necessary to extend the life of air-driven machinery like valves and air motors. Lubricator units are not necessarily necessary, though, as the majority of pneumatic systems are self-lubricating.
A Prep System for Air:
Pneumatic air preparation devices are often installed in the following order, going from upstream to downstream:
- valve for system isolation
- Lubricator/Regulator and Filter (if needed)
- shut-off valve for devices
Users can choose the precise set of devices required for their application. Since regulation usually comes before filtration, the filter must be rated to manage supply air pressure. The majority of these functions, except for lubrication, can be obtained using total air preparation equipment. In comparison to the more active downstream pneumatics components, air preparation design is simple but simple to ignore. Years of dependable performance from a pneumatic system are ensured by proper air preparation. In contrast to the more active downstream components of pneumatics, such as automated valves and actuators, air preparation is not difficult but is simple to overlook. In all circumstances, making sure that correct air preparation is in place results in years of reliable and trouble-free pneumatic operation. Get more information about industrial measurement equipment in Pakistan by consulting the experience of SS Hussain.